“It’s pointless having a website if no-one can find it!”
Before we continue, I’d just like to state that there is no Silver Bullet about SEO, these recommendations come from personal experiments. The algorithms that rank the pages are not publicly available and even though I might mention Google as a synonym for search engine, you should always consider who you’re targeting. E.g. Yahoo has a relevant share in the US compared to the UK, and Baidu is the “Google” in China.
So what is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
“SEO is a way of creating more visibility on Search Engines such as Google, Bing! and Baidu, by ranking websites higher in search results, which in turn lead to more click-troughs and conversions.”
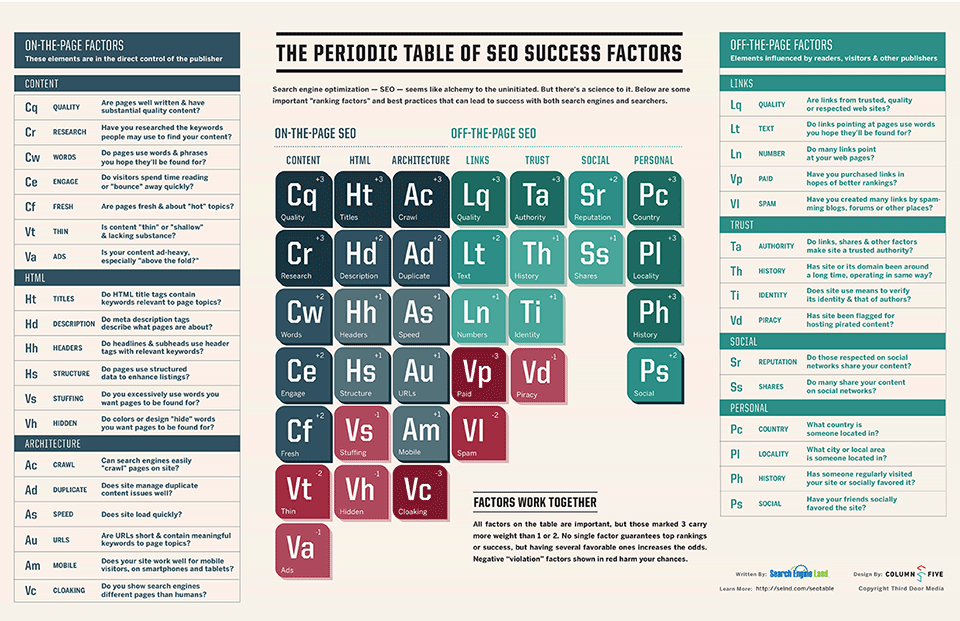
To improve your Search Engine Results Page (SERP) ranking, there are on-the-page factors like Code / Markup and Content, and off-the-page factors, such as Links / Social. By ranking higher in the SERP, you increase your visibility and reputation, which in turn lead to sales / engagement. See below a great infographic about SEO.
Technical Improvements – Why should I care?
Although the Technical Improvements have the smallest impact of the improvements I’ll be mentioning in terms of reputation, they are the first step to get your website pages visible / indexed.
Case-study – shopcade.com
Shopcade is a social / e-commerce platform (something like Facebook meets Amazon). At the time they had a catalog of 100M products, but only a fraction of those products were indexed / discoverable, so the mission was to get most of the catalog showing up on the SERPs.
After implementing most of the technical improvements (code / markup), the site went from 34K indexed pages to 85M on Google in a year! I believe I have your attention now…
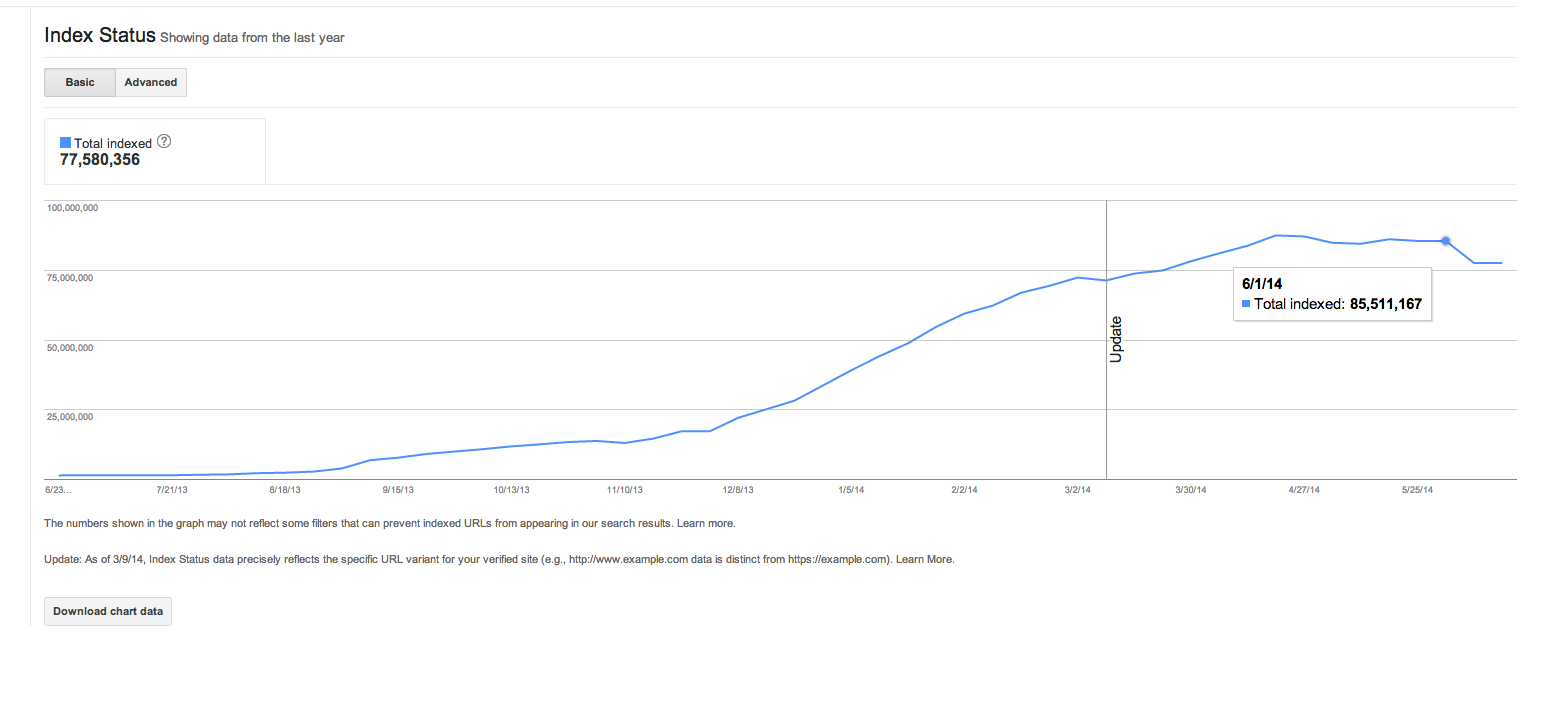
We got this graph from Google Webmaster Tools (GWT) and we could monitor which improvements had better results (we also added comments on Google Analytics every time we made an improvement, so we could track better).
Crawlers / Bots / Spiders
A Web crawler is an Internet bot which systematically browses the World Wide Web, typically for the purpose of Web indexing. A Web crawler may also be called a Web spider, a bot, an ant or an automatic indexer.
A spider is a program run by a search engine to build a summary of a website’s content (content index). Spiders create a text-based summary of content and an address (URL) for each webpage.
Below is an example of how Humans perceive a webpage. We can clearly understand what is important, what is the title, and where is the Call to Action (CTA), etc.

And below is an example of how a Spider would “understand” the same website. So we need to make use of the appropriate HTML tags to help the spiders understand the content and importance of the page, by using title tags, semantic tags, and because they don’t “read” the images content, alt tags for images.

Technical Improvements – What can I do?
- Setup the “robots.txt” to allow “crawlers” to index your pages
Improper configuration might prevent the pages to be indexed
- Avoid User-Agent Cloaking
By showing different content depending on the User-Agent the site might be penalized
- Improve site speed
Slower sites will be penalised. See more on Why should we care about website performance
- Every image should have an “alt” attribute
This helps the automated “crawlers” understand the content of the images
- Every page should have a canonical URL and make use of pagination meta tags
The Canonical URL is the owner of the content, even if there are multiple URLs that serve the same content. This avoids penalization for content duplication. e.g. <link rel=“canonical” href=“http://example.com/page-a”>. Pagination tags example <link rel=“next” …> and <link rel=“previous” …>
- Make use of http redirection (301) when necessary to avoid duplicate content
e.g., http://www.example.com, https://www.example.com, http://example.com, http://example.com/ should all redirect to only one of them, like https://www.example.com/, this avoids content duplication, which means multiple pages serving the exact same content. An alternative is to make use of the canonical meta tag.
- Make use of the HTML5 semantic Tags
Use tags like article, section, aside, summary, …
- Use H1-H6 in order to demonstrate hierarchy
H1 being the most important to H6 the least
- Add a Meta Title tag
This should be relevant to the actual content of the page. Should not be longer than 50-60 characters, as Google truncates the rest in the search results. You should avoid duplicate meta titles
- Add a Meta Description tag
This should be relevant to the actual content of the page. Should not be longer than 150-160 characters, as Google truncates the rest in the search results. You should avoid duplicate meta descriptions
- Avoid broken links and have a helpful 404 (page not found) error page
Whenever a page is moved, we should implement a 301 (permanent) redirection to the new page to keep the same value as it had before (link juice). 404 pages should return the http status 404 and should have useful links back into the site. Broken Links are bad User Experience (UX) therefore penalized.
- Add Social Meta Tags (Facebook Open Graph, Twitter Cards, and Google Publisher)
These tags, help the spider to understand the content of the website, and allow those companies to better represent the content of the page on a snippet. Google Publisher will eventually add more credibility to the site, by showing your latest posts and profile on the top right side of the search results page
- Submit sitemaps regularly
Submitting sitemaps helps the Search Engines to be aware of your latest pages, updates, etc
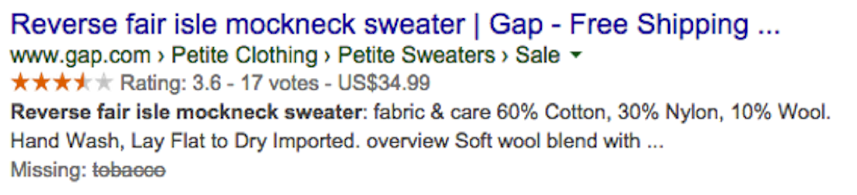
- Make use of rich snippets by using Microformat, Schema.org, …
By using this special markup, “spiders” will be able to better understand the content and provide rich snippets on the search results. Available formats can describe a Product, a Person, Comments, Reviews, etc. Also take advantage of Google Now Cards by using schema.org for email (airline ticket, bills, …).
Below an example of a rich snippet with ratings, price, …
- Think Mobile
Optimize the website for mobile, by creating a specific mobile website when possible. Search results vary if made from a desktop or from a mobile device
- Use Google Analytics (GA) and Google Webmaster Tools (GWT)
They provide very insightful data about how is your site performing. GWT also provides SEO recommendations
- SEO friendly URL structure
Which one is sexier? http://example.com/page.php?p=918726 or http://example.com/awesome-article
The URL string is also searchable, which helps your page to be discoverable.
Avoid making the URLs too deep, if it takes many clicks to get there, then the content is less relevant or important. Also, if we make categories like http://example.com/product/product-name, http://example.com/product/ should also be available as a page that contains products… URLS are case sensitive
Below we have an example of URLs being highlighted in search results:

How do I know my site is being indexed?
So, after implementing those improvements, it’s time to see if they’re working.
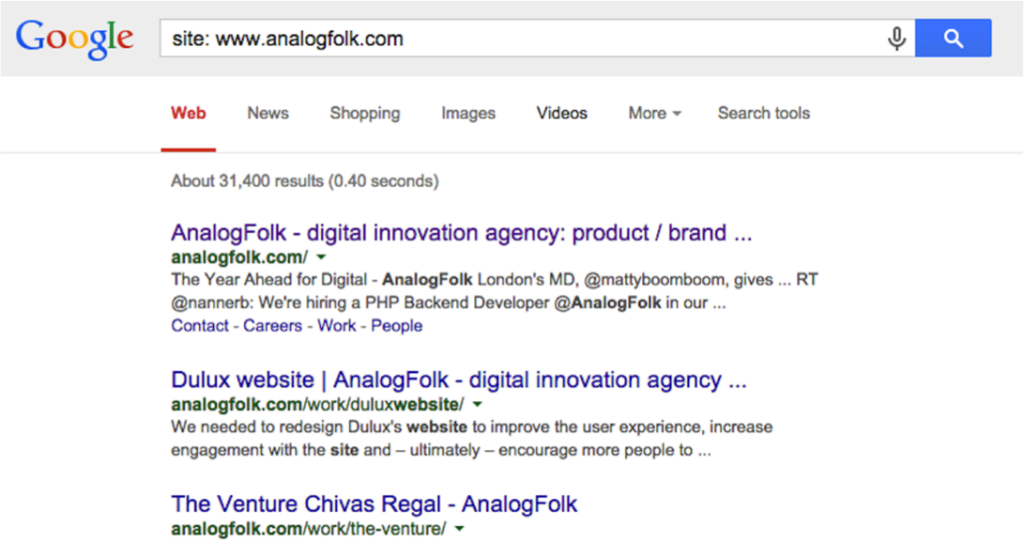
Getting your site indexed is just one of the steps. You can verify that your site is being indexed by searching for “site: www.sitename.com”
Content – Why should I care?
Now that we’re sure the site is being indexed, we want to rank higher than our competitors for the selected keywords. About 85% of the users find what they’re looking for in the 1st search results page. We should clearly define which keywords are relevant to our content, e.g. Lucozade as a keyword vs energy drink or feeling down… If a user searches for the brand, they will already know what they want, so we should try to target the related keywords in order to increase discoverability.
Case-study shopcade.com
The website was being properly indexed, but performing poorly (not showing on the top results).
By implementing a series of non-technical improvements, Shopcade consistently started to rank even higher than the actual brand that also sold the products, consequently improving the click-through rate by 50% – 80%.
Content – What can I do?
- Content is King
Write fresh, well written, unique quality content. One of the most important factors for SEO. Sell through content
- Start a Blog
Use the blog to keep users engaged and add more content. Use the blog to cross-sell some products / articles. Some blog are engaging and funny, and as a side effect, they lead users into your website
- Inform the client
Users who are informed are more likely to buy. As an example, we have the eBay Buying Guides, that explain what to look for in a certain product. They also use it as an opportunity to cross-sell by suggesting a few products
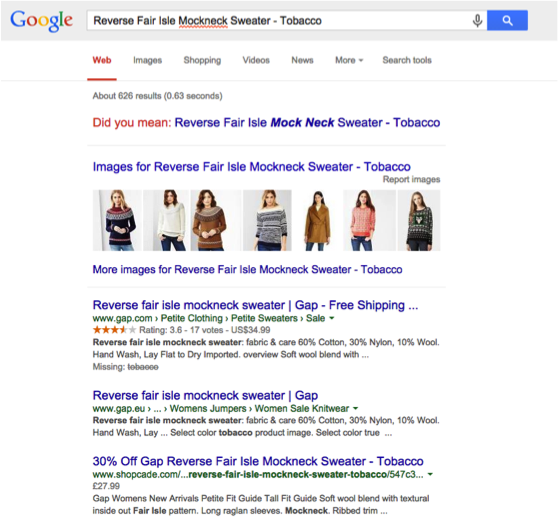
- Tweak the page title to provide more information about the product
e.g. simply prepending “35% Off” Product Name on the Shopcade product pages title, made the users click this site instead of others
- Link Juice
Keep users engaged by suggesting similar/recent/top products/articles. This means users will spend more time on the site and more likely to come back. It also allows Search Engines to discover your content more easily. Create lists about your products, create articles like Who the famous “TV SERIES” Are you? – Target the intended keywords to drive traffic into your site
- Allow users to add comments / reviews
Not only it adds unique content and freshness, it also helps other users to make the purchase / keep engaged. Be aware of spam comments and links (you should considering adding “nofollow” to those links). One of the downsides of allowing users to add comments is risk of being bullied by the users, and it might imply an overhead due to moderation
- Use Google Trends and other similar tools
Find out which keywords are trending and create content around it to try to capture a few more users into your website and then convert them. E.g. Super Bowl, create an article or a product list targeting the competition, and them try to convert the users
- Use Google Webmaster Tools
Find out how your users are discovering your website and try to explore it even further. Either by creating content around it or by doing more of what is currently converting better
- Target long tail queries
Easier to rank due to less competition and the more specific the higher the intention. E.g. “Adidas Originals ZX Flux” as opposed to “adidas running shoes”
Links / Social – What can I do?
“Each link back to your site is a vote…”
- Social Media
Share your articles / content in Social Media accounts and allow users to share and spread the word. Consider owning a #hashtag. Create competitions to keep users engaged and go viral
- Link Building / Establish Relations
Engage other users / bloggers to write content / reviews about your product (should be natural and not paid)
- Link Quality
Authority website links will count more than regular and “spammy” websites
- Link Without Any Conditions
All links should feel natural. Having links to other websites, is like voting for those websites. Avoid linking to spammy websites and don’t impose linking back
What have I missed? Feel free to comment.